What do you know about food additives?
As the Codex food additives meeting continues in Jinan, China, we spoke to FAO Senior Food Safety Officer Markus Lipp about the need and use for additives in food and who decides if they are safe.
What do food additives do?
Food additives are substances that have a specific function. For example, they make the food safer by preventing microbiological spoilage, they can be used to colour food or make the flavour, smell, taste, even texture more appealing. Some additives are designed to facilitate food preparation, for those who desire it, e.g. self-rising flour, ready-to-use salad dressing. Food additives have been in use for centuries, such as plain salt to preserve fish or curing salt to make meat last longer. Similarly, the resins added to Greek or Roman wine acted as mild preservatives.
Why do we need food additives?
They can be part of a sustainable food system – to maintain the freshness and appeal or improve the shelf-life and nutritional values of foods.
Is it safe to use food additives?
With the increasing use of processed foods, food additives are more widely used. However, like for any other aspect of human society, scientific evolution brings new data to the discussion table. For example, boric acid was used as a food preservative until World War II, but it was later prohibited due to its toxicity. Today, in almost all countries the safety of food additives has to be determined prior to their use. National authorities, may use JECFA or their own assessments to demonstrate the scientific basis for the safe use of these additives.
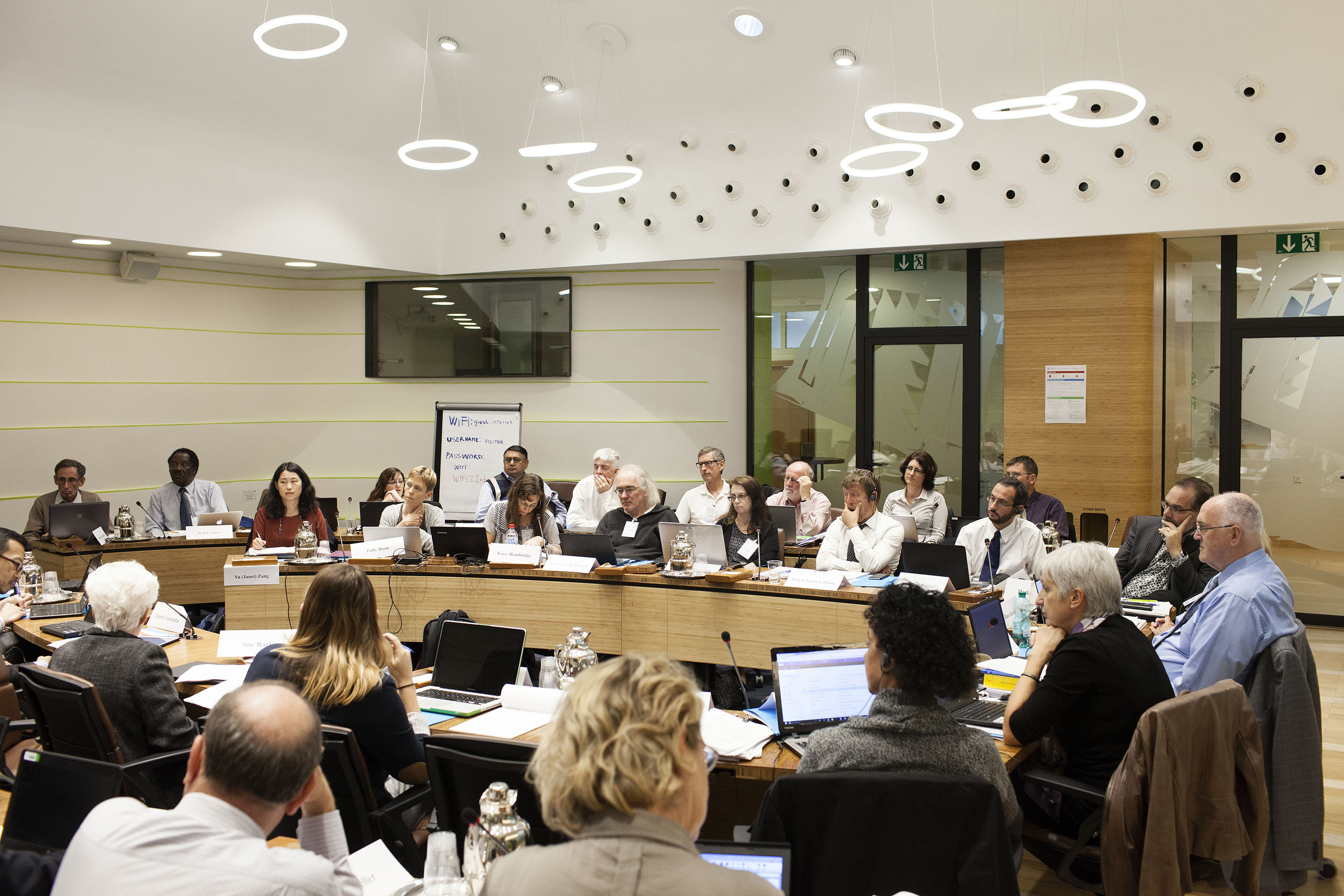

JECFA meeting, Rome, Italy ©FAO/Giuseppe Carotenuto
You mentioned JECFA -what is that?
JECFA is an international body of experts run jointly by FAO and WHO that is responsible for determining whether food additives are safe for human consumption. JECFA is comprised of scientific experts from many scientific disciplines and many parts of the world. The experts are identified through a worldwide public call, which is followed be careful screening process.
How does it work?
JECFA experts review all available chemical, biochemical, toxicological, technological and any other relevant data on a given additive. The toxicological evaluations consider the possible short-term as well as long-term health effects to determine the maximum amount an individual food additive may be used in food. Once a food additive has been found to be safe by JECFA, its maximum permitted use level in food is recorded in the Codex General Standard for Food Additives.
What does that have to do with trade?
More and more food is traded internationally and transported over long distances regionally. Codex standards can facilitate the import and export of food by providing a common understanding and a dictionary of terms to all trading partners. The World Trade Organization (WTO) relies on the standards, guidelines and recommendations set by the Codex Alimentarius Commission to ensure food safety. In addition to food additives, the standards address all other aspects of modern food production, including veterinary drug and pesticide residues, contaminants, methods of analysis and sampling and hygiene.
Video
Watch how JECFA evaluates the safety of food additives.
Learn more about JECFA in FAO and WHO
Read the WHO fact sheet on food additives
Consult the Codex General Standard on Food Additives
At the heart of the Codex mandate are the core values of collaboration, inclusiveness, consensus building and transparency. Governmental and non-governmental, public and private organizations alike play a vital role in ensuring Codex texts are of the highest quality and based on sound science.
Codex would have little authority in the field of international standard setting if it did not welcome and acknowledge the valuable contributions made by observers. Expert technical bodies, industry and consumer associations
contribute to the standard-setting process in a spirit of openness, collaboration and transparency.
Intergovernmental organizations (IGOs) and international non-governmental organizations (NGOs) can apply for observer status in Codex in order to attend and put forward their views at every stage of the standard-setting process.
 Current Codex Alimentarius Commission
Current Codex Alimentarius Commission
What do you know about food additives?
As the Codex food additives meeting continues in Jinan, China, we spoke to FAO Senior Food Safety Officer Markus Lipp about the need and use for additives in food and who decides if they are safe.
What do food additives do?
Food additives are substances that have a specific function. For example, they make the food safer by preventing microbiological spoilage, they can be used to colour food or make the flavour, smell, taste, even texture more appealing. Some additives are designed to facilitate food preparation, for those who desire it, e.g. self-rising flour, ready-to-use salad dressing. Food additives have been in use for centuries, such as plain salt to preserve fish or curing salt to make meat last longer. Similarly, the resins added to Greek or Roman wine acted as mild preservatives.
Why do we need food additives?
They can be part of a sustainable food system – to maintain the freshness and appeal or improve the shelf-life and nutritional values of foods.
Is it safe to use food additives?
With the increasing use of processed foods, food additives are more widely used. However, like for any other aspect of human society, scientific evolution brings new data to the discussion table. For example, boric acid was used as a food preservative until World War II, but it was later prohibited due to its toxicity. Today, in almost all countries the safety of food additives has to be determined prior to their use. National authorities, may use JECFA or their own assessments to demonstrate the scientific basis for the safe use of these additives.

JECFA meeting, Rome, Italy ©FAO/Giuseppe Carotenuto
You mentioned JECFA -what is that?
JECFA is an international body of experts run jointly by FAO and WHO that is responsible for determining whether food additives are safe for human consumption. JECFA is comprised of scientific experts from many scientific disciplines and many parts of the world. The experts are identified through a worldwide public call, which is followed be careful screening process.
How does it work?
JECFA experts review all available chemical, biochemical, toxicological, technological and any other relevant data on a given additive. The toxicological evaluations consider the possible short-term as well as long-term health effects to determine the maximum amount an individual food additive may be used in food. Once a food additive has been found to be safe by JECFA, its maximum permitted use level in food is recorded in the Codex General Standard for Food Additives.
What does that have to do with trade?
More and more food is traded internationally and transported over long distances regionally. Codex standards can facilitate the import and export of food by providing a common understanding and a dictionary of terms to all trading partners. The World Trade Organization (WTO) relies on the standards, guidelines and recommendations set by the Codex Alimentarius Commission to ensure food safety. In addition to food additives, the standards address all other aspects of modern food production, including veterinary drug and pesticide residues, contaminants, methods of analysis and sampling and hygiene.
Video
Watch how JECFA evaluates the safety of food additives.
Learn more about JECFA in FAO and WHO
Read the WHO fact sheet on food additives
Consult the Codex General Standard on Food Additives
 Codex and Observer
Codex and Observer
around the world since ancient times.
We might not always know where it comes from,
but we expect it to be available, safe and of good quality.








Leave a comment