WHO on AMR and Codex
Q&A with WHO: Kazuaki Miyagishima and Awa Aidara-Kane
The Codex Alimentarius Commission agreed in July 2016 to re-establish the Intergovernmental Task Force on Antimicrobial Resistance in order to revise and update the Codex code of practice on AMR and to set guidelines for integrated AMR surveillance that can be adopted by Codex member countries.
Q: What are the WHO expectations for the Task Force meeting?
A: Codex responded to the demand from the international community by agreeing to launch new work in two areas: (1) updating the existing guidance on how to minimize and contain antimicrobial resistance arising from food production, and (2) new guidance on the integrated surveillance on antimicrobial resistance, linking data on the use of antibiotics in animals and in humans on one hand and the prevalence of resistant bacteria in samples from animals, food and humans as well as the environment. The former is important especially because WHO published new guidelines on 7 November. Codex is invited to take on board any pertinent recommendations from these guidelines and build them into a Codex text. The second will be also important as it will help us keep track of the evolution of situations and will inform future revisions of guidance from WHO and Codex.
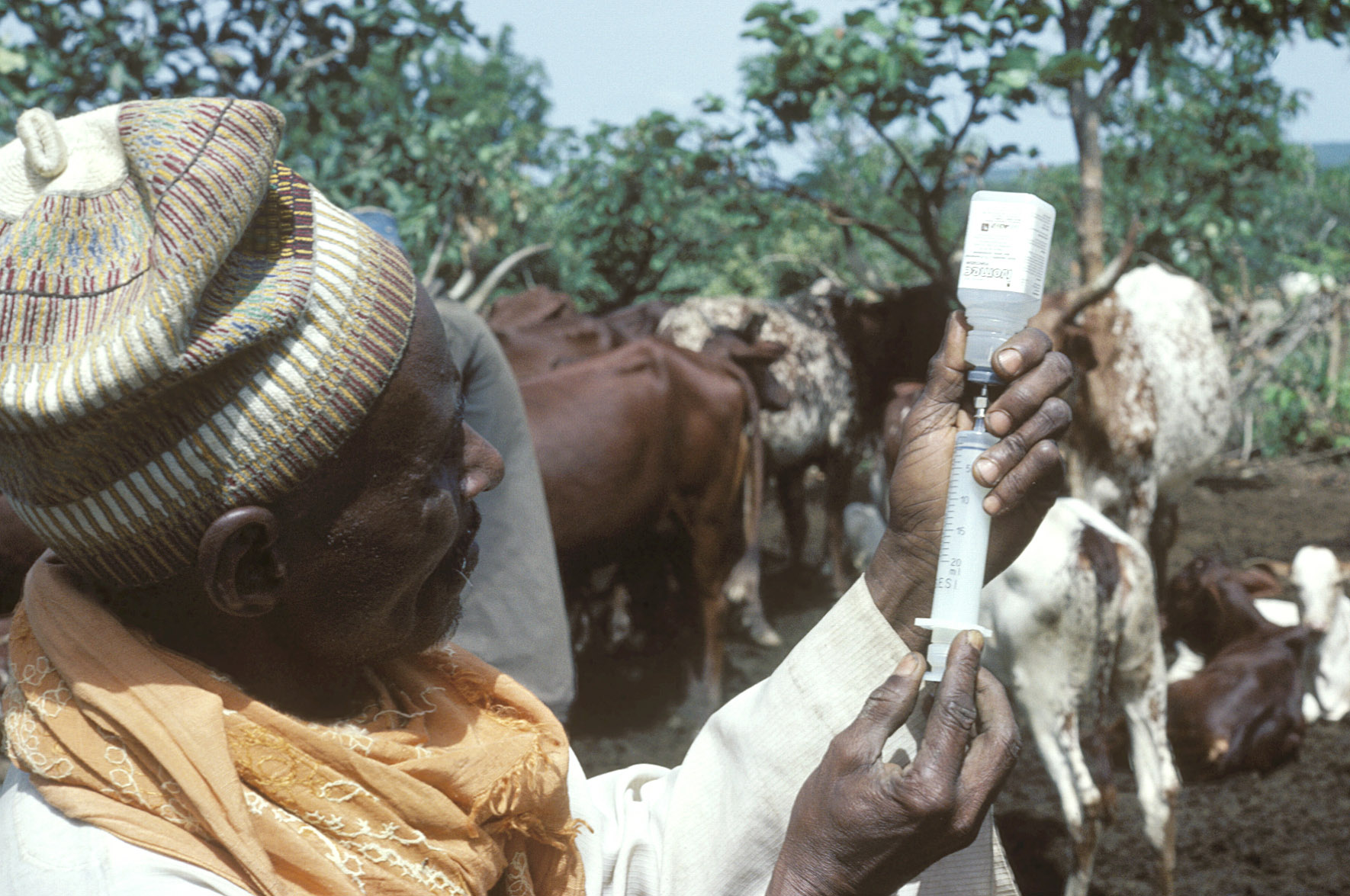

Central African Republic - Peul herdsman tending sick cattle.
Policy and action
WHO says that placing global emphasis on surveillance and evidence based research will inform policies and actions that Member States and intergovernmental agencies can take to address the growing health security challenges of antimicrobial resistance.
Q: How can Codex work impact this objective?
A: By developing new guidance on the integrated surveillance on antimicrobial resistance, linking data on the use of antibiotics in animals and in humans on one hand and the prevalence of resistant bacteria in samples from animals, food and humans as well as the environment. This will be important as it will help us keep track of the evolution of situations and will inform future revisions of guidance from WHO and Codex. WHO published in June this year an updated guidance document on the integrated surveillance, which Codex can get inspiration from.
National Action Plans
The World Health Assembly urged all Member States to develop and have in place by 2017, national action plans on antimicrobial resistance that are aligned with the objectives of the global action plan.
Q: What aspects of a national action plan for AMR are of particular relevance for Codex?
A: The aspects of the AMR National Action Plans of relevance to Codex are those related to objective 2 (surveillance of antimicrobial resistance) and objective 3 (optimal use of antimicrobials) of the Global Action Plan.
Link:
WHO and AMR - follow the campaign.
At the heart of the Codex mandate are the core values of collaboration, inclusiveness, consensus building and transparency. Governmental and non-governmental, public and private organizations alike play a vital role in ensuring Codex texts are of the highest quality and based on sound science.
Codex would have little authority in the field of international standard setting if it did not welcome and acknowledge the valuable contributions made by observers. Expert technical bodies, industry and consumer associations
contribute to the standard-setting process in a spirit of openness, collaboration and transparency.
Intergovernmental organizations (IGOs) and international non-governmental organizations (NGOs) can apply for observer status in Codex in order to attend and put forward their views at every stage of the standard-setting process.
 Current Codex Alimentarius Commission
Current Codex Alimentarius Commission
WHO on AMR and Codex
Q&A with WHO: Kazuaki Miyagishima and Awa Aidara-Kane
The Codex Alimentarius Commission agreed in July 2016 to re-establish the Intergovernmental Task Force on Antimicrobial Resistance in order to revise and update the Codex code of practice on AMR and to set guidelines for integrated AMR surveillance that can be adopted by Codex member countries.
Q: What are the WHO expectations for the Task Force meeting?
A: Codex responded to the demand from the international community by agreeing to launch new work in two areas: (1) updating the existing guidance on how to minimize and contain antimicrobial resistance arising from food production, and (2) new guidance on the integrated surveillance on antimicrobial resistance, linking data on the use of antibiotics in animals and in humans on one hand and the prevalence of resistant bacteria in samples from animals, food and humans as well as the environment. The former is important especially because WHO published new guidelines on 7 November. Codex is invited to take on board any pertinent recommendations from these guidelines and build them into a Codex text. The second will be also important as it will help us keep track of the evolution of situations and will inform future revisions of guidance from WHO and Codex.

Central African Republic - Peul herdsman tending sick cattle.
Policy and action
WHO says that placing global emphasis on surveillance and evidence based research will inform policies and actions that Member States and intergovernmental agencies can take to address the growing health security challenges of antimicrobial resistance.
Q: How can Codex work impact this objective?
A: By developing new guidance on the integrated surveillance on antimicrobial resistance, linking data on the use of antibiotics in animals and in humans on one hand and the prevalence of resistant bacteria in samples from animals, food and humans as well as the environment. This will be important as it will help us keep track of the evolution of situations and will inform future revisions of guidance from WHO and Codex. WHO published in June this year an updated guidance document on the integrated surveillance, which Codex can get inspiration from.
National Action Plans
The World Health Assembly urged all Member States to develop and have in place by 2017, national action plans on antimicrobial resistance that are aligned with the objectives of the global action plan.
Q: What aspects of a national action plan for AMR are of particular relevance for Codex?
A: The aspects of the AMR National Action Plans of relevance to Codex are those related to objective 2 (surveillance of antimicrobial resistance) and objective 3 (optimal use of antimicrobials) of the Global Action Plan.
Link:
WHO and AMR - follow the campaign.
 Codex and Observer
Codex and Observer
around the world since ancient times.
We might not always know where it comes from,
but we expect it to be available, safe and of good quality.








Leave a comment