Technical Barriers to Trade meeting at WTO in Geneva
WTO Members are meeting this week in Geneva to discuss technical barriers to trade. Specific trade concerns on food labelling, food certification, nutrition, organic production, alcoholic drinks and halal foods are on the agenda and all areas where Codex standards can help ensure fair practices in trade.
What are Technical Barriers to Trade?
Technical Barriers to Trade are measures adopted by governments establishing product requirements for fulfilment of public policy objectives, such as human health and safety, environmental protection, consumer information, or quality. These measures apply to both domestically produced and imported goods.
Under the Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Agreement, members are free to choose how to regulate products to achieve those objectives but must do so in a way that does not discriminate between trading partners or that does not unnecessarily restrict trade in these products.
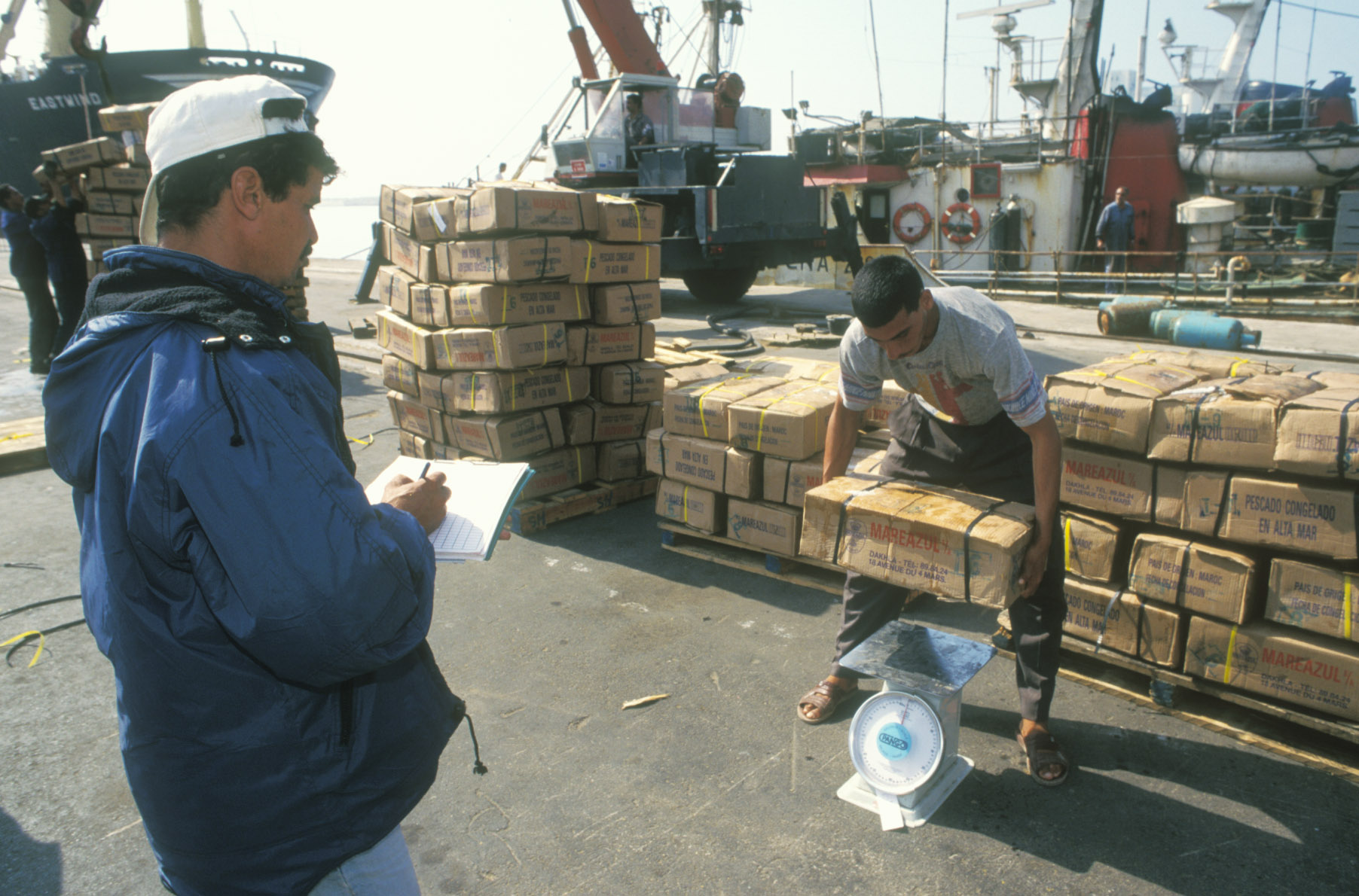

Boxes of frozen fish being weighed and inspected by a customs officer at Agadir port - Morocco.
The WTO strongly encourages members to base their measures on international standards to facilitate trade and to ensure that they do not create unnecessary trade barriers or arbitrarily or unjustifiably discriminate between members.
The Committee usually holds three formal meetings per year. Meetings are open to all WTO members and observer governments. International intergovernmental organizations — several of them standardizing bodies (including Codex) — also participate as observers in the Committee.
Trade in all goods
The TBT Agreement covers trade in all goods – agricultural and industrial alike – and applies to three categories of measures: technical regulations such as product characteristics or labelling requirements; standards, and conformity assessment procedures - which are used to determine that relevant requirements in technical regulations or standards are fulfilled.
Apart from the food related issues highlighted above, the meeting will include discussions on a wide range of topics, from cyber security and cosmetics, to pneumatic tyres and toy safety.
How does it work?
WTO members/observers use the TBT Committee to discuss specific trade concerns (STCs) — specific laws, regulations or procedures that affect their trade. Members raise STCs to find out more about the scope and implementation of another country’s regulations. The discussion is mostly about measures that a member is planning to introduce, but can also be about the implementation of existing measures. The TBT Information Management System TBT IMS is a database of WTO information on TBT notifications and specific trade concerns.
Keeping Codex standards up to date
Items of particular interest to Codex at this session include food labelling, alcoholic drinks, energy drinks, halal food and infant formula.
Patrick Sekitoleko, Codex Food Standards Officer attending the current session in Geneva said: “Participating as an observer in the WTO Committee on TBT allows the Codex Secretariat to follow discussions that could have implications for ongoing and future Codex work and helps us ensure that our standards are up to date and dealing with real and relevant issues for our members.”
Learn more
https://www.wto.org/english/tratop_e/tbt_e/tbt_e.htm
Download the FAO/WTO publication Trade and Food Standards.
At the heart of the Codex mandate are the core values of collaboration, inclusiveness, consensus building and transparency. Governmental and non-governmental, public and private organizations alike play a vital role in ensuring Codex texts are of the highest quality and based on sound science.
Codex would have little authority in the field of international standard setting if it did not welcome and acknowledge the valuable contributions made by observers. Expert technical bodies, industry and consumer associations
contribute to the standard-setting process in a spirit of openness, collaboration and transparency.
Intergovernmental organizations (IGOs) and international non-governmental organizations (NGOs) can apply for observer status in Codex in order to attend and put forward their views at every stage of the standard-setting process.
 Current Codex Alimentarius Commission
Current Codex Alimentarius Commission
Technical Barriers to Trade meeting at WTO in Geneva
WTO Members are meeting this week in Geneva to discuss technical barriers to trade. Specific trade concerns on food labelling, food certification, nutrition, organic production, alcoholic drinks and halal foods are on the agenda and all areas where Codex standards can help ensure fair practices in trade.
What are Technical Barriers to Trade?
Technical Barriers to Trade are measures adopted by governments establishing product requirements for fulfilment of public policy objectives, such as human health and safety, environmental protection, consumer information, or quality. These measures apply to both domestically produced and imported goods.
Under the Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Agreement, members are free to choose how to regulate products to achieve those objectives but must do so in a way that does not discriminate between trading partners or that does not unnecessarily restrict trade in these products.

Boxes of frozen fish being weighed and inspected by a customs officer at Agadir port - Morocco.
The WTO strongly encourages members to base their measures on international standards to facilitate trade and to ensure that they do not create unnecessary trade barriers or arbitrarily or unjustifiably discriminate between members.
The Committee usually holds three formal meetings per year. Meetings are open to all WTO members and observer governments. International intergovernmental organizations — several of them standardizing bodies (including Codex) — also participate as observers in the Committee.
Trade in all goods
The TBT Agreement covers trade in all goods – agricultural and industrial alike – and applies to three categories of measures: technical regulations such as product characteristics or labelling requirements; standards, and conformity assessment procedures - which are used to determine that relevant requirements in technical regulations or standards are fulfilled.
Apart from the food related issues highlighted above, the meeting will include discussions on a wide range of topics, from cyber security and cosmetics, to pneumatic tyres and toy safety.
How does it work?
WTO members/observers use the TBT Committee to discuss specific trade concerns (STCs) — specific laws, regulations or procedures that affect their trade. Members raise STCs to find out more about the scope and implementation of another country’s regulations. The discussion is mostly about measures that a member is planning to introduce, but can also be about the implementation of existing measures. The TBT Information Management System TBT IMS is a database of WTO information on TBT notifications and specific trade concerns.
Keeping Codex standards up to date
Items of particular interest to Codex at this session include food labelling, alcoholic drinks, energy drinks, halal food and infant formula.
Patrick Sekitoleko, Codex Food Standards Officer attending the current session in Geneva said: “Participating as an observer in the WTO Committee on TBT allows the Codex Secretariat to follow discussions that could have implications for ongoing and future Codex work and helps us ensure that our standards are up to date and dealing with real and relevant issues for our members.”
Learn more
https://www.wto.org/english/tratop_e/tbt_e/tbt_e.htm
Download the FAO/WTO publication Trade and Food Standards.
 Codex and Observer
Codex and Observer
around the world since ancient times.
We might not always know where it comes from,
but we expect it to be available, safe and of good quality.








Leave a comment