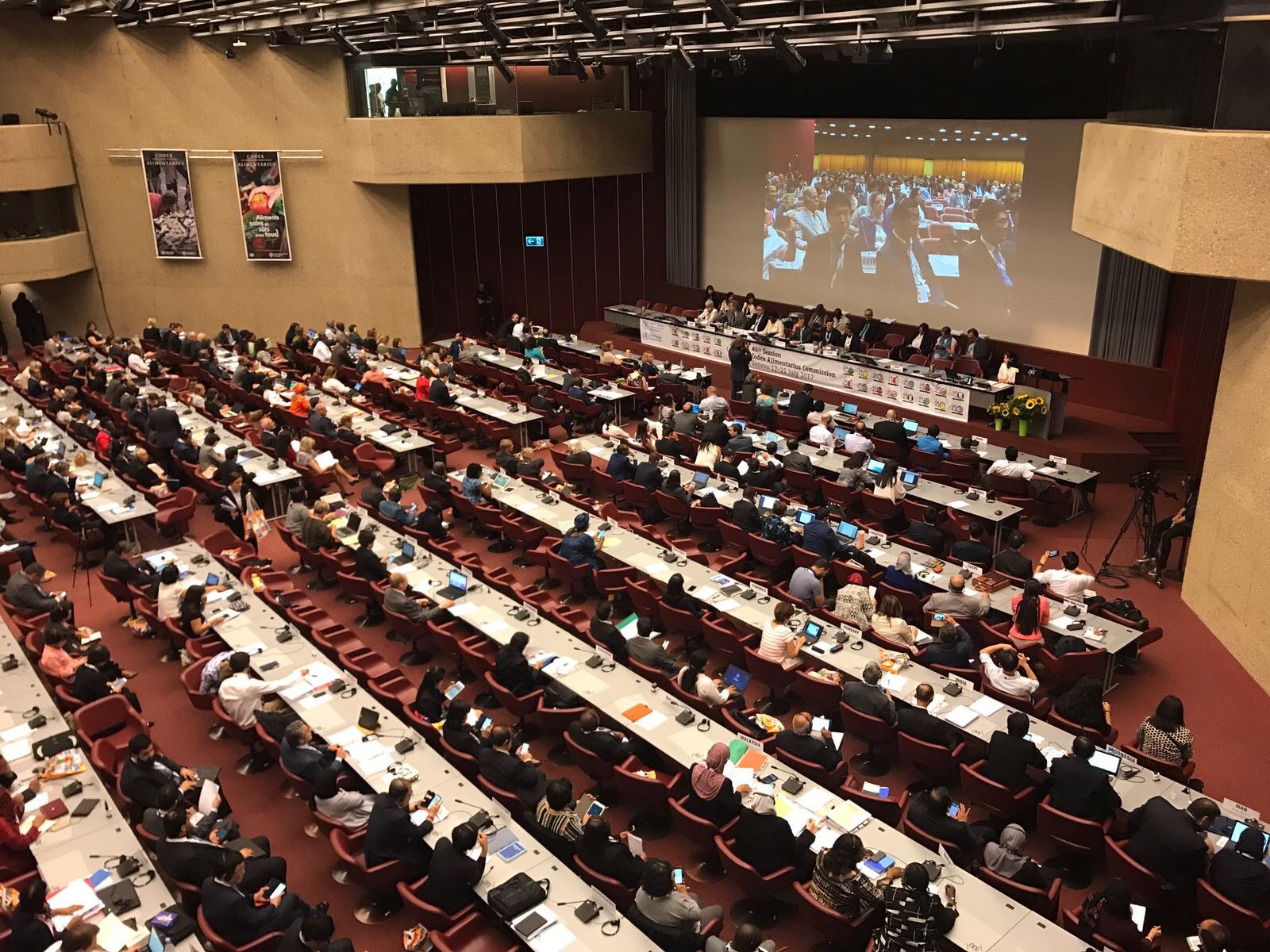
Billions benefit from the work of Codex
In Geneva delegates from 136 countries are meeting to approve international food standards to protect consumers and ensure fair practices in the food trade.
Codex: one of the most successful joint ventures in the UN system.
Oleg Chestov
As CAC40 opened today in Geneva, Dr Oleg Chestnov, WHO Assistant Director-General, Noncommunicable Diseases and Mental Health welcomed delegates and underlined the importance of the successful partnership formed in Codex by FAO and WHO. With major tasks on the horizon such as combatting antimicrobial resistance and reaching the Sustainable Development Goals he described the Commission, as "one of the most successful joint ventures in the UN system".
Dr Ren Wang, Assistant Director-General, Agriculture and Consumer Protection Department, FAO, echoed the words of the recent G20 in Hamburg in his opening remarks and underlined “the crucial role of the rules-based international trading system”. Dr Wang reminded delegates that a country needs to be able to "speak the scientific language of the international standard setting community," and for that "adequate strategic investment in national capacities for food control is required".
The Codex Chairperson Mrs Awilo Ochieng Pernet congratulated the Commission on the decision by FAO to adopt a resolution that would make June 7th International Food Safety Day. She stressed the importance of such a day in raising awareness about the importance of food safety and in contributing to enhancing consumer health protection.

Standards adopted on day one.
Highlights of the work on day one include agreement on maximum residue limits for a range of drugs sometimes used in food-producing animals. The decision was based on an evaluation by the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA).
Maximum residue limits were set for medicines Ivermectin (used to kill parasites) in tissues from cattle, and Lasalocid sodium (used for a similar purpose) in tissues from birds (chicken, turkey, quail and pheasant). Also, maximum residue limits were set for the insecticide Teflubenzuron when used in salmon.
Code of hygienic practice for fresh fruits and vegetables
Codex also adopted revisions updating its risk-based Code of Hygienic Practice for Fresh Fruits and Vegetables (CAC/RCP 53-2003) to provide detailed guidance to stakeholders along fresh fruit and vegetable value chains - from producers through to final consumers.
Production, handling and preparation of all foods involves various risks. These can be reduced by following good agricultural and hygienic practices to help control microbial, chemical and physical hazards. This, in turn, minimizes the likelihood of foodborne diseases affecting consumers or negatively impacting public health. Such risks apply equally to fresh fruits and vegetables.
Over 50 standards and other texts are proposed for adoption at this 40th Session of the Commission plus more than 30 new work proposals to develop standards. Work continues until Saturday.
Live webcast
Follow the 40th Commission live in six languages via our webcast. Click here.
At the heart of the Codex mandate are the core values of collaboration, inclusiveness, consensus building and transparency. Governmental and non-governmental, public and private organizations alike play a vital role in ensuring Codex texts are of the highest quality and based on sound science.
Codex would have little authority in the field of international standard setting if it did not welcome and acknowledge the valuable contributions made by observers. Expert technical bodies, industry and consumer associations
contribute to the standard-setting process in a spirit of openness, collaboration and transparency.
Intergovernmental organizations (IGOs) and international non-governmental organizations (NGOs) can apply for observer status in Codex in order to attend and put forward their views at every stage of the standard-setting process.
 Current Codex Alimentarius Commission
Current Codex Alimentarius Commission
Billions benefit from the work of Codex
In Geneva delegates from 136 countries are meeting to approve international food standards to protect consumers and ensure fair practices in the food trade.
Codex: one of the most successful joint ventures in the UN system.
Oleg Chestov
As CAC40 opened today in Geneva, Dr Oleg Chestnov, WHO Assistant Director-General, Noncommunicable Diseases and Mental Health welcomed delegates and underlined the importance of the successful partnership formed in Codex by FAO and WHO. With major tasks on the horizon such as combatting antimicrobial resistance and reaching the Sustainable Development Goals he described the Commission, as "one of the most successful joint ventures in the UN system".
Dr Ren Wang, Assistant Director-General, Agriculture and Consumer Protection Department, FAO, echoed the words of the recent G20 in Hamburg in his opening remarks and underlined “the crucial role of the rules-based international trading system”. Dr Wang reminded delegates that a country needs to be able to "speak the scientific language of the international standard setting community," and for that "adequate strategic investment in national capacities for food control is required".
The Codex Chairperson Mrs Awilo Ochieng Pernet congratulated the Commission on the decision by FAO to adopt a resolution that would make June 7th International Food Safety Day. She stressed the importance of such a day in raising awareness about the importance of food safety and in contributing to enhancing consumer health protection.

Standards adopted on day one.
Highlights of the work on day one include agreement on maximum residue limits for a range of drugs sometimes used in food-producing animals. The decision was based on an evaluation by the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA).
Maximum residue limits were set for medicines Ivermectin (used to kill parasites) in tissues from cattle, and Lasalocid sodium (used for a similar purpose) in tissues from birds (chicken, turkey, quail and pheasant). Also, maximum residue limits were set for the insecticide Teflubenzuron when used in salmon.
Code of hygienic practice for fresh fruits and vegetables
Codex also adopted revisions updating its risk-based Code of Hygienic Practice for Fresh Fruits and Vegetables (CAC/RCP 53-2003) to provide detailed guidance to stakeholders along fresh fruit and vegetable value chains - from producers through to final consumers.
Production, handling and preparation of all foods involves various risks. These can be reduced by following good agricultural and hygienic practices to help control microbial, chemical and physical hazards. This, in turn, minimizes the likelihood of foodborne diseases affecting consumers or negatively impacting public health. Such risks apply equally to fresh fruits and vegetables.
Over 50 standards and other texts are proposed for adoption at this 40th Session of the Commission plus more than 30 new work proposals to develop standards. Work continues until Saturday.
Live webcast
Follow the 40th Commission live in six languages via our webcast. Click here.
 Codex and Observer
Codex and Observer
around the world since ancient times.
We might not always know where it comes from,
but we expect it to be available, safe and of good quality.








Leave a comment