Codex approves 39 standards in 2016
All new and revised Codex texts now available on line.
The Codex mandate is to develop harmonised international food standards, which protect consumer health and promote fair practices in food trade.
The 39th Commission held last July in Rome, adopted 39 Codex texts (Standards, Guidelines and Codes of Practice)
If national governments adopt these standards, as with all Codex standards then barriers to trade are removed and all consumers can benefit from safe food of good quality.
One of the new standards deals with nutrition labelling and another with information excahnges in international trade
Nutrient values on food labels
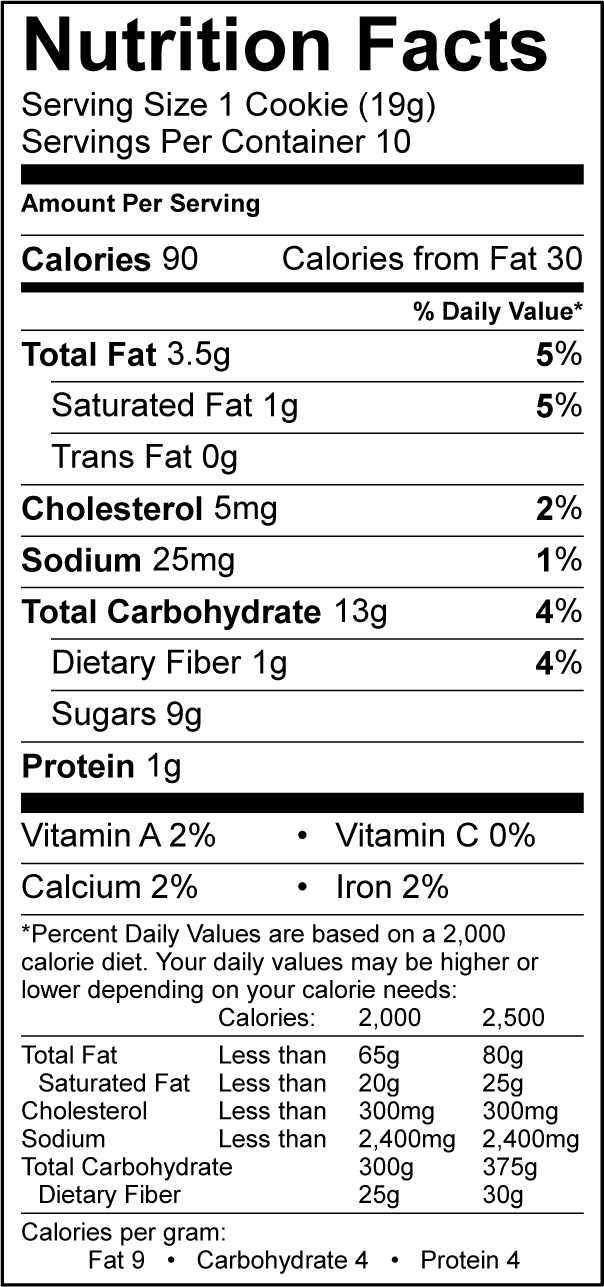
According to the Codex Guidelines on Nutrition Labelling the amounts of the vitamins and minerals present in the food should be declared on the label of prepackaged food.
The Codex Committee for Nutrition and Special Dietry Uses (CCNFSDU) proposed a series of NRVs-R (Nutrient Reference Values – Requirements) for copper, iron, magnesium, phosphorus and Vitamin A at the Commission. They were adopted, marking the third batch of NRVs-R for vitamins and minerals adopted following previous submissions in 2013 and in 2014.
NRVs-R are used in the nutrition labelling of foods. They refer to the daily reference intakes for vitamins and minerals for an adult population. According to the Codex Guidelines on Nutrition Labelling the amounts of the vitamins and minerals present in the food should be declared on the label of prepackaged food.
Numerical information on vitamins and minerals should be expressed in metric units and/or as a percentage of the NRV.
What is an NRV?
The Chair of the committee Dr Pia Noble explained NRVs. She said: "To give an example: if the label declares that the vitamin C content of 100g of the food is 50% of the NRV; this means consuming 100g of the food provides 50% of the daily required amount of vitamin C. This is important information to help consumers to choose those foods that suit their individual dietary needs and contribute to an overall healthful dietary intake."
Dr Noble also explained some of the work that has gone into the revision of the existing NRVs-R in the Guideline on Nutrition Labelling and the Elaboration of NRVs-R for certain vitamins and minerals, established for the first time and based on the newest scientific data.
"This has been a complex and demanding task. CCNFSDU decided to follow a step by step process and has now been working on this project for several years. I hope that we can finalize our work at the next session of CCNFSDU in December 2016 at which we have to decide on the NRVs-R for Vitamin D and Vitamin E."
Principles and guidelines for the exchange of information between importing and exporting countries to support the trade in food
Together with developing international standards for safe food of good quality, the Codex mandate also involves working to ensure fair practices in food trade. The Codex Committee on Food Import and Export Inspection and Certification Systems (CCFICS) this year concluded work on how countries communciate with one another to speed up trade without compromising safety.
CCFICS is hosted by Australia and the host secretariat said: "the development of this guidance in such a short timeframe is a credit to Codex and highlights its ability to address emerging issues and the needs of members in a timely manner with a high level of engagement.
"This work is highly relevant to the international trading environment. The guidance developed is to assist the competent authority of the importing and exporting countries to identify when the exchange of information may be necessary and what information is essential for the assessment of the relevant component(s) of the National Food Control Systems and to simplify and harmonize the information exchange process."
The guidance will be valuable in assisting countries to improve their import and export systems.
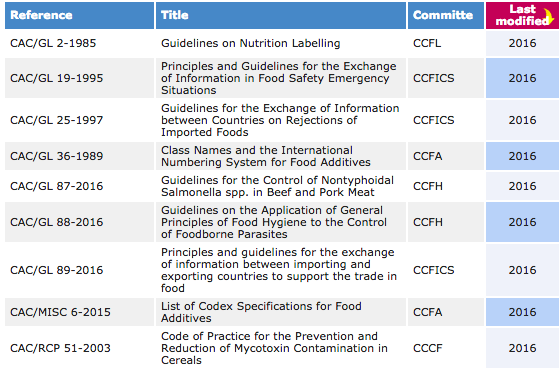
For a complete list of Codex texts developed in 2016 go to the list of standards on the Codex website.
At the heart of the Codex mandate are the core values of collaboration, inclusiveness, consensus building and transparency. Governmental and non-governmental, public and private organizations alike play a vital role in ensuring Codex texts are of the highest quality and based on sound science.
Codex would have little authority in the field of international standard setting if it did not welcome and acknowledge the valuable contributions made by observers. Expert technical bodies, industry and consumer associations
contribute to the standard-setting process in a spirit of openness, collaboration and transparency.
Intergovernmental organizations (IGOs) and international non-governmental organizations (NGOs) can apply for observer status in Codex in order to attend and put forward their views at every stage of the standard-setting process.
 Current Codex Alimentarius Commission
Current Codex Alimentarius Commission
Codex approves 39 standards in 2016
All new and revised Codex texts now available on line.
The Codex mandate is to develop harmonised international food standards, which protect consumer health and promote fair practices in food trade.

The 39th Commission held last July in Rome, adopted 39 Codex texts (Standards, Guidelines and Codes of Practice)
If national governments adopt these standards, as with all Codex standards then barriers to trade are removed and all consumers can benefit from safe food of good quality.
One of the new standards deals with nutrition labelling and another with information excahnges in international trade
Nutrient values on food labels
According to the Codex Guidelines on Nutrition Labelling the amounts of the vitamins and minerals present in the food should be declared on the label of prepackaged food.

The Codex Committee for Nutrition and Special Dietry Uses (CCNFSDU) proposed a series of NRVs-R (Nutrient Reference Values – Requirements) for copper, iron, magnesium, phosphorus and Vitamin A at the Commission. They were adopted, marking the third batch of NRVs-R for vitamins and minerals adopted following previous submissions in 2013 and in 2014.
NRVs-R are used in the nutrition labelling of foods. They refer to the daily reference intakes for vitamins and minerals for an adult population. According to the Codex Guidelines on Nutrition Labelling the amounts of the vitamins and minerals present in the food should be declared on the label of prepackaged food.
Numerical information on vitamins and minerals should be expressed in metric units and/or as a percentage of the NRV.
What is an NRV?
The Chair of the committee Dr Pia Noble explained NRVs. She said: "To give an example: if the label declares that the vitamin C content of 100g of the food is 50% of the NRV; this means consuming 100g of the food provides 50% of the daily required amount of vitamin C. This is important information to help consumers to choose those foods that suit their individual dietary needs and contribute to an overall healthful dietary intake."
Dr Noble also explained some of the work that has gone into the revision of the existing NRVs-R in the Guideline on Nutrition Labelling and the Elaboration of NRVs-R for certain vitamins and minerals, established for the first time and based on the newest scientific data.
"This has been a complex and demanding task. CCNFSDU decided to follow a step by step process and has now been working on this project for several years. I hope that we can finalize our work at the next session of CCNFSDU in December 2016 at which we have to decide on the NRVs-R for Vitamin D and Vitamin E."
Principles and guidelines for the exchange of information between importing and exporting countries to support the trade in food
Together with developing international standards for safe food of good quality, the Codex mandate also involves working to ensure fair practices in food trade. The Codex Committee on Food Import and Export Inspection and Certification Systems (CCFICS) this year concluded work on how countries communciate with one another to speed up trade without compromising safety.
CCFICS is hosted by Australia and the host secretariat said: "the development of this guidance in such a short timeframe is a credit to Codex and highlights its ability to address emerging issues and the needs of members in a timely manner with a high level of engagement.
"This work is highly relevant to the international trading environment. The guidance developed is to assist the competent authority of the importing and exporting countries to identify when the exchange of information may be necessary and what information is essential for the assessment of the relevant component(s) of the National Food Control Systems and to simplify and harmonize the information exchange process."
The guidance will be valuable in assisting countries to improve their import and export systems.
For a complete list of Codex texts developed in 2016 go to the list of standards on the Codex website.
 Codex and Observer
Codex and Observer
around the world since ancient times.
We might not always know where it comes from,
but we expect it to be available, safe and of good quality.








Leave a comment