Codex in the supply chain
It is peak bloom season and a beautiful time of year at the foot of Mt Hood in Oregon USA - about a one hour drive from Portland through the Columbia River Gorge.
A documentary team from Flooded Cellar in the UK is currently filming there to look at Codex Alimentarius throughout the supply chain. This involves speaking directly to farmers and manufacturers as well as industry and consumers.
The visit has been coordinated by the U.S. Codex Office and the Food Safety and Inspection Service (FSIS) within the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA).

Crop Spraying
The tractor applies a spray to control fireblight on the pear blossoms. There is a critical need for pesticides in agriculture, and the farmer has to understand international standards (Codex) to make pesticide application decisions. Getting this right is important for exports and to support the local economy. Indeed having standards in place in export markets is a critical piece of the process.

Measuring the effects of pesticides
Pest management is also crucial and the specialist can be seen evaluating applications of pesticide for research. Gathering scientific data is needed to set the Maximum Residue Levels (MRLs) that are the basis of Codex standards in this field.
Field representatives from the pesticide producers coordinate between the growers and the packhouses to determine where the fruit is likely to be marketed or exported. They help the growers make decisions about what pesticides to use, and what pre-harvest interval to follow, in order to ensure compliance with international trade standards.
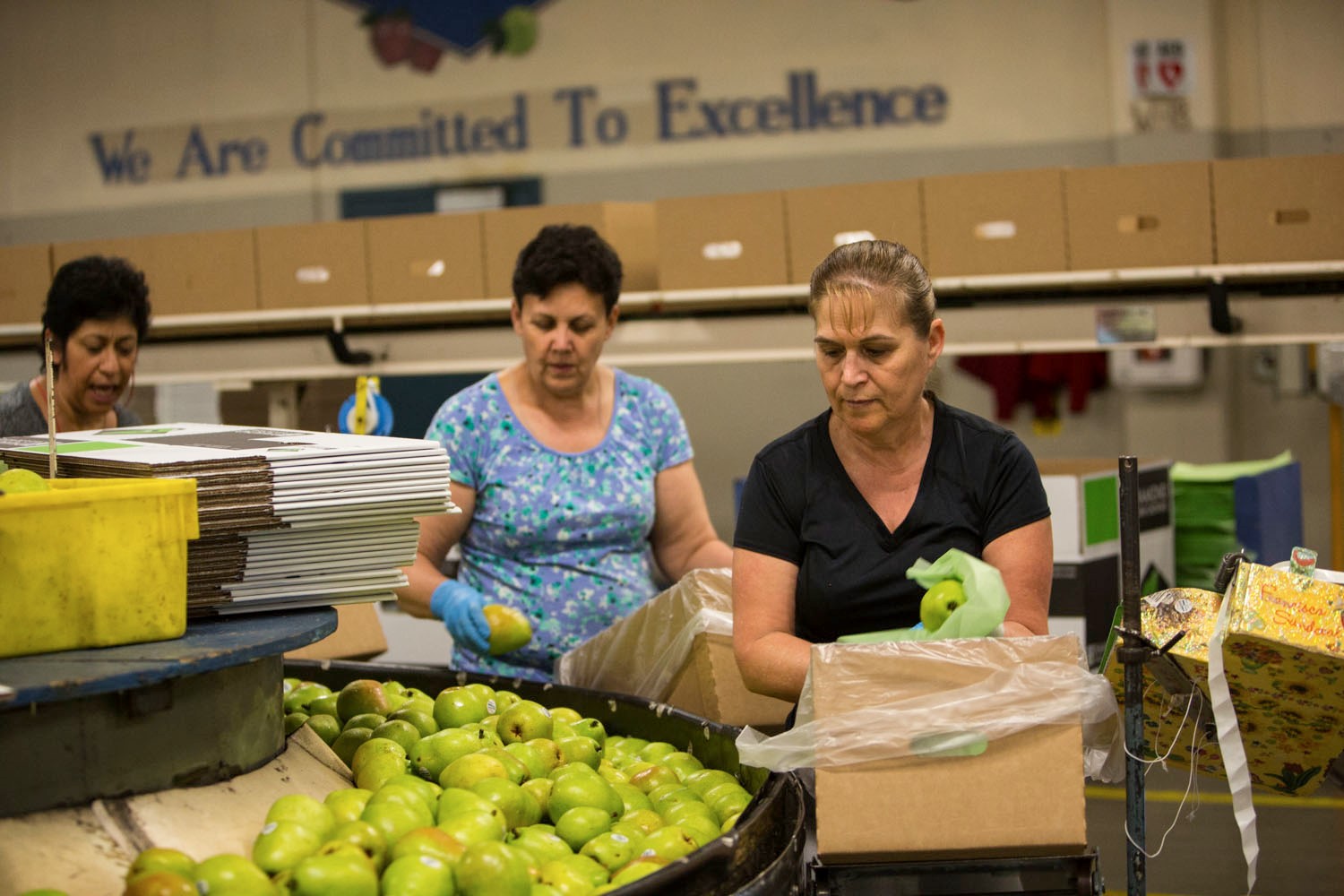

At the pear packhouse
As the prodcue is packed for export, it is critical there are standards in place in the chosen export markets to ensure that no trade disruptions occur. Industry also needs to ensure that growers are following spray regulations in order to comply with both US and Codex MRLs.
Learn more
Click on the link to examine the Codex Pesticides database of MRLs.
The full documentary will be available shortly online
At the heart of the Codex mandate are the core values of collaboration, inclusiveness, consensus building and transparency. Governmental and non-governmental, public and private organizations alike play a vital role in ensuring Codex texts are of the highest quality and based on sound science.
Codex would have little authority in the field of international standard setting if it did not welcome and acknowledge the valuable contributions made by observers. Expert technical bodies, industry and consumer associations
contribute to the standard-setting process in a spirit of openness, collaboration and transparency.
Intergovernmental organizations (IGOs) and international non-governmental organizations (NGOs) can apply for observer status in Codex in order to attend and put forward their views at every stage of the standard-setting process.
 Current Codex Alimentarius Commission
Current Codex Alimentarius Commission
Codex in the supply chain

It is peak bloom season and a beautiful time of year at the foot of Mt Hood in Oregon USA - about a one hour drive from Portland through the Columbia River Gorge.
A documentary team from Flooded Cellar in the UK is currently filming there to look at Codex Alimentarius throughout the supply chain. This involves speaking directly to farmers and manufacturers as well as industry and consumers.
The visit has been coordinated by the U.S. Codex Office and the Food Safety and Inspection Service (FSIS) within the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA).

Crop Spraying
The tractor applies a spray to control fireblight on the pear blossoms. There is a critical need for pesticides in agriculture, and the farmer has to understand international standards (Codex) to make pesticide application decisions. Getting this right is important for exports and to support the local economy. Indeed having standards in place in export markets is a critical piece of the process.

Measuring the effects of pesticides
Pest management is also crucial and the specialist can be seen evaluating applications of pesticide for research. Gathering scientific data is needed to set the Maximum Residue Levels (MRLs) that are the basis of Codex standards in this field.
Field representatives from the pesticide producers coordinate between the growers and the packhouses to determine where the fruit is likely to be marketed or exported. They help the growers make decisions about what pesticides to use, and what pre-harvest interval to follow, in order to ensure compliance with international trade standards.

At the pear packhouse
As the prodcue is packed for export, it is critical there are standards in place in the chosen export markets to ensure that no trade disruptions occur. Industry also needs to ensure that growers are following spray regulations in order to comply with both US and Codex MRLs.
Learn more
Click on the link to examine the Codex Pesticides database of MRLs.
The full documentary will be available shortly online
 Codex and Observer
Codex and Observer
around the world since ancient times.
We might not always know where it comes from,
but we expect it to be available, safe and of good quality.








Leave a comment